WASTE & EFFLUENT MANAGEMENT
Waste
GRI Standards
| GRI 306: Waste | Section/Comments | |
|---|---|---|
| GRI 103-1 | Management approach: Explanation of the material topic and its boundary | |
| GRI 103-2 | Management approach: The management approach and its components |
Material aspects & scope |
| GRI 103-3 | Management approach: Evaluation of the management approach | |
| GRI 306-1 | Waste generation and significant waste-related impacts | |
| GRI 306-2 | Management of significant waste-related impacts | Thrust Areas: For Judicious Waste Management |
| GRI 306-3 | Waste generated | Specific Hazardous Waste Generation: 2.31 Kg/KL of FG |
| GRI 306-4 | Waste diverted from disposal | |
| GRI 306-5 | Waste directed to disposal | |
Conscious waste management has become pivotal for every business as it not only impacts the ecology but also has a hit on business growth due to its management cost. We realise that our operations generate a significant quantity of waste; both hazardous as well as non-hazardous and therefore we adopt industry best practices and set challenging goals for effective waste management. As a sustainability objective, KNPL took an incremental target of 5% reduction of our Specific Hazardous Waste Generation (SHWG) year-on-year.
Thrust Areas: For Judicious Waste Management
- Dedicated storage for category-wise waste in scrap yard across all plants
- Systematic tracking of the quantity of waste generated and waste disposed
- Ensure proper waste disposal – diverting waste away from landfill
- Imbibing the principle of 3R – Reduce, Reuse and Recycle
- Sensitisation of employees on waste handling methods
Waste Generated
In FY 2021-22, our organisation-wide total waste generation was 12,579 MT, of which 827 MT was hazardous waste, 21 MT was E-waste, 0.09 MT was bio-medical waste while the rest was non-hazardous waste.
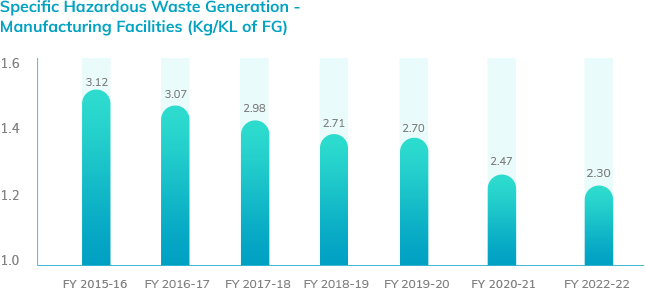
Our organisation-wide Specific Hazardous Waste Generation (SHWG) was 2.31 Kg/KL of FG while our Specific Hazardous Waste Generation for our manufacturing facilities accounted to 2.30 Kg/KL of FG
Hazardous waste generated due to our operations mainly includes distillation residue, Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) sludge, paint sludge, dirty resin, contaminated barrel/tins, filter cartridge, and contaminated cotton waste.
Method of Calculation:
a) Manufacturing Facilities - Specific Hazardous Waste Generation is ratio of
hazardous waste generated in Plants to Production of Finished Goods during specified
period.
b) Organisation-wide - Specific Hazardous Waste Generation is ratio of hazardous
waste generated in Plants and R&D centre to Production of Finished Goods during
specified period.
Waste Disposal
At KNPL, the waste generated is segregated and then disposed as per statutory requirement and applicable norms to authorised Treatment, Storage and Disposal Facilities (TSDFs), who then dispose, reuse or recycle it as applicable. We have been successful in diverting most of our hazardous waste away from landfill through adoption of co-processing of hazardous waste to cement kilns.
Waste Diverted From Disposal
- Reusable cartridge in the filtration process
- Cleaning solvents of all major resins are reused in the next batch of same resins
- In paint section, system controls have been implemented to ensure reuse of paint filled in part filled cans in the next compatible batch of paint
- In operations, cleaning solvent is reused after distillation process again for equipment cleaning
- Paint Pigging wash water reuse
- TiO2 recovery through de-dusting
- Reusing drums and barrels
- Take-back mechanism with suppliers supplying raw materials in plastic bags
Waste Directed to Disposal
- Barrels/Tins are recycled through authorised vendors
- Plastic waste, corrugated boxes and metal scrap generated within factory premises is recycled through authorised vendors
- Raw materials procured in recyclable packaging material
- E-waste sent through buy-back programme
Plastic Waste Management
At KNPL, we have taken concerted efforts to reduce our plastic waste generation through our manufacturing facilities. Through rigorous due-diligence process and constant communication, we encourage suppliers to substitute plastic with alternate materials or implement a take back mechanism. During the reporting period, we ensured zero procurement and usage of packing material less than the thickness limit in microns set by the regulatory bodies.
Extended Producer Responsibility
We, at KNPL, have initiated our efforts to meet the targets laid under EPR and tackle the challenge of eliminating plastic waste from the ecosystem to the maximum extent. We are currently in the process of our registering ourselves on the newly launched centralised e-portal by Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB). We have also associated with external agency to ensure diligent collection, treatment and disposal of postconsumer plastic waste in line with the EPR target and maximum traceability.
Effluent Treatment
GRI Standards
| GRI 306: Effluents and Waste | Section/Comments | |
|---|---|---|
| GRI 103-1 | Management approach: Explanation of the material topic and its boundary |
Material aspects & scope |
| GRI 103-2 | Management approach: The management approach and its components | |
| GRI 103-3 | Management approach: Evaluation of the management approach | |
| GRI 306-1 | Water discharge by quality and destination | Effluent treatment |
| GRI 306-2 | Waste by type and disposal method | We have a dedicated storage for category-wise waste in scrapyard across all plants. The waste generated is segregated and then disposed as per statutory requirement to authorised Treatment, Storage and Disposal Facilities (TSDFs), who then dispose, reuse or recycle it as applicable. |
| GRI 306-3 | Significant spills | During the year, there were no cases of significant spillage at any of our manufacturing sites. |
| GRI 306-4 | Transport of hazardous waste | No hazardous waste transported internationally. All are disposed to local authorised TSDF. Material and waste management |
| GRI 306-5 | Water bodies affected by water discharges and/or runoff | All major facilities are zero effluent discharge; hence water bodies are not affected adversely |
Keeping Our Waters Clean
Zero Liquid Discharge: Our two-way approach of Reduction at source and Reuse has enabled us to be a Zero Liquid Discharge Organisation.
Installed dedicated treatment facilities for domestic and industrial effluents across all our plants
Our industrial effluents are treated in Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) and then passed through Reverse Osmosis (RO) and Multi Effect Evaporator (MEE)
All plants are equipped with in-house laboratory to monitor the quality of effluent to ensure compliance with Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and State Pollution Control Board (SPCB) norms